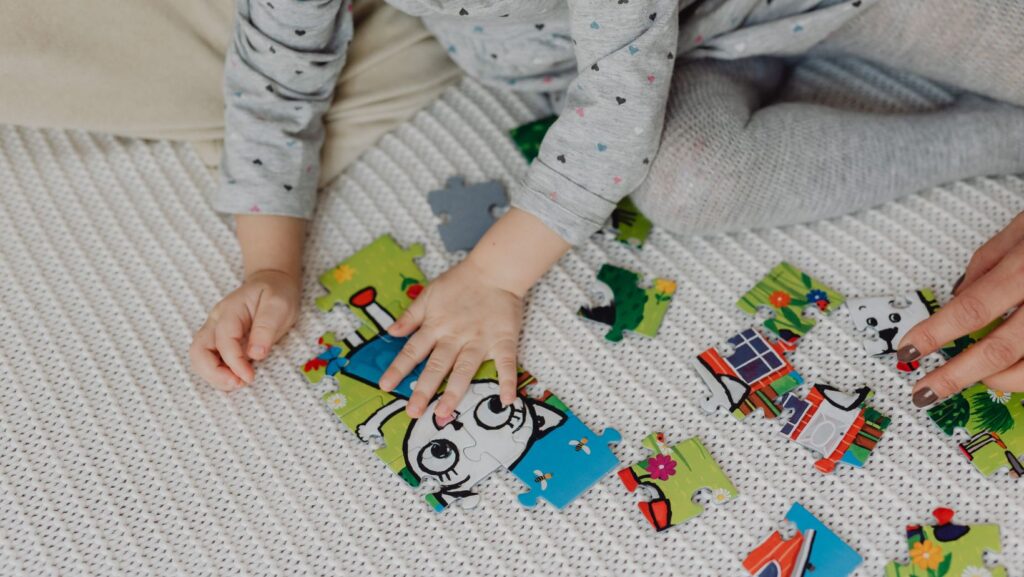
Puzzles and blocks are powerful tools in occupational therapy (OT) for children. These simple yet versatile objects engage kids in activities that promote crucial developmental skills. Through play with puzzles and blocks, children enhance their fine motor skills, problem-solving abilities, and spatial reasoning.
Puzzles offer a unique blend of challenge and reward. As children manipulate puzzle pieces, they develop hand-eye coordination and finger dexterity. The act of fitting pieces together stimulates cognitive processes, encouraging persistence and logical thinking. Blocks, on the other hand, allow for open-ended exploration. Stacking, sorting, and building with blocks help children refine their grasp, improve hand strength, and understand spatial relationships.
Occupational therapists leverage these toys to create engaging sessions that feel like playtime for children. The repetitive nature of puzzle-solving and block-building provides opportunities for therapists to observe and guide skill development. As kids progress from simple to more complex puzzles and block structures, they gain confidence and independence in their abilities. To read more about occupational therapy activities that incorporate these tools, explore resources tailored for therapists and parents.
Disclaimer: This material is intended for general information and should not replace personalized medical care. Please reach out to a healthcare professional for specific guidance.
Key Takeaways
- Puzzles and blocks enhance fine motor skills and cognitive development in children
- These toys provide engaging, play-based opportunities for skill-building in OT sessions
- Occupational therapists use puzzles and blocks to promote independence and confidence in young clients
Engagement and Development Through Puzzles
Puzzles offer a wealth of benefits for children, promoting cognitive growth, visual skills, motor development, and social-emotional learning. These engaging activities provide opportunities for holistic development in fun and interactive ways.
Cognitive and Problem-Solving Skills
Puzzles challenge children’s minds and foster critical thinking. As kids manipulate pieces and search for solutions, they develop logical reasoning and strategic planning abilities. Jigsaw puzzles, in particular, require children to analyze shapes, colors, and patterns to complete the image.
Problem-solving skills flourish as children encounter obstacles and devise strategies to overcome them. This process enhances their ability to approach challenges systematically and persevere through difficulties.
Puzzles also boost memory skills. Children must remember the overall picture, piece shapes, and previously attempted combinations to progress efficiently.
Visual Perceptual Skills Enhancement
Puzzle play significantly improves visual perception and processing. Children learn to distinguish between similar shapes and colors, enhancing their visual discrimination abilities. This skill is crucial for reading, writing, and mathematics.
Visual memory improves as kids recall the positions of pieces and the overall puzzle design. Spatial awareness develops through manipulating and rotating pieces to fit them correctly.
Visual closure skills are honed when children identify partially hidden or incomplete images. This ability aids in recognizing letters and words quickly during reading.
Fine Motor Skills and Coordination
Puzzles provide excellent opportunities for fine motor development. Grasping, manipulating, and placing small pieces require precise finger movements and control. These actions strengthen hand muscles and improve dexterity.
Eye-hand coordination improves as children align pieces with specific spots. This skill transfers to activities like writing, drawing, and using utensils.
Motor planning skills develop as kids strategize how to pick up, rotate, and place pieces. This ability supports daily tasks like dressing and using tools.
Emotional and Social Benefits
Completing puzzles boosts children’s self-esteem and confidence. The sense of accomplishment upon finishing a challenging puzzle motivates kids to tackle new tasks.
Puzzles teach patience and persistence. Children learn to manage frustration and maintain focus on long-term goals.
Group puzzle-solving promotes social skills. Kids practice turn-taking, sharing, and communicating ideas. Collaborative problem-solving fosters teamwork and mutual support.
Puzzles can also aid emotional regulation. The focused, repetitive nature of puzzle-solving can have a calming effect, helping children manage stress and anxiety.
Influence of Blocks on Occupational Therapy Outcomes
Blocks serve as versatile tools in occupational therapy, enhancing various aspects of child development. They promote physical, cognitive, and social-emotional growth through engaging play activities.
Physical Skills and Building Blocks
Building blocks significantly impact fine and gross motor skills. Children develop hand-eye coordination as they grasp, stack, and manipulate blocks of different sizes. This activity strengthens finger muscles, which are crucial for tasks like writing and buttoning clothes.
Occupational therapists use block play to improve bilateral coordination. Children learn to use both hands together, enhancing their ability to perform daily tasks. Stacking tall towers or creating complex structures challenges balance and core strength.
Block activities also foster motor planning skills. Kids must think ahead, considering block placement and structure stability. This planning translates to improved sequencing in everyday activities.
Creativity, Imagination, and Pretend Play
Block play sparks creativity and imagination. Children transform simple shapes into elaborate structures, vehicles, or characters. This imaginative process encourages problem-solving and flexible thinking.
Pretend play with blocks allows kids to explore different scenarios and roles. They might build a castle and act out royal adventures or create a city and become construction workers. This type of play supports emotional development and social skills.
Occupational therapists observe how children engage in independent play with blocks. It provides insights into their cognitive processes and ability to self-direct activities.
Spatial Awareness and Cognitive Growth
Block play enhances spatial awareness and reasoning. Children learn concepts like “above,” “below,” “next to,” and “between” as they construct. This spatial understanding is crucial for math skills and navigating the physical world.

Sorting blocks by shape, size, or color promotes cognitive development. It helps children recognize patterns and categorize objects, skills that transfer to academic learning.
Problem-solving is inherent in block play. Kids must figure out how to balance blocks, create symmetry, or achieve a specific design. These challenges foster critical thinking and persistence.
Language Skills and Learning Enhancement
Block play naturally encourages communication. Children often narrate their building process or describe their creations, expanding their vocabulary. They learn terms related to shapes, sizes, and spatial relationships.
Occupational therapists may use blocks to reinforce literacy skills. They might label blocks with letters or words, integrating reading practice into play. This multisensory approach supports language development.
Following instructions to build specific structures helps improve listening skills and comprehension. It also introduces concepts of sequencing, which are important for storytelling and organizing thoughts.
Conclusion
Puzzles and blocks serve as powerful tools in occupational therapy for children. They enhance cognitive abilities, fine motor skills, and problem-solving capabilities in engaging ways. These activities foster development across multiple domains while providing enjoyable learning experiences. Integrating puzzles and blocks into OT sessions can yield significant benefits for a child’s overall growth and skill acquisition.
